
-
How it works
-
Industries
-
Services
-
Material
-
Company
-
Resources











 Industries
Industries
Instantly calculate the cost for predefined models. Simply select a model, choose your desired material, and adjust the size and other specifications to see how much the printing will cost in real time.
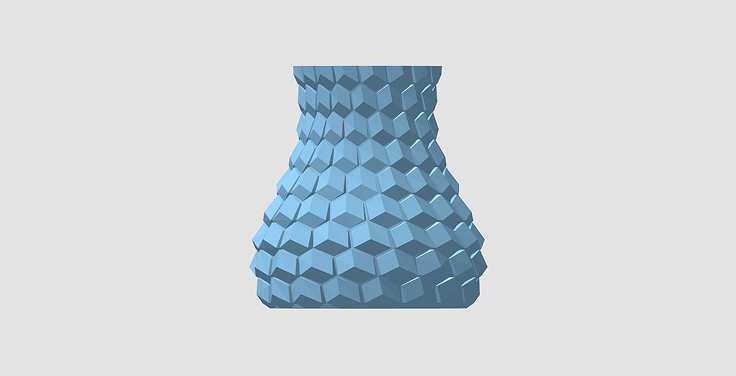
Prices are estimates and may vary based on final dimensions and material selection.
| Dimensions | 110 x 110 x 114 mm |
| Volume | 83 cc |
| Weight | 102.92 g |
| Lead Time | 2 days |
| Item Price | ₹820.04 |
| GST | ₹147.61 |
| Total | ₹967.65 |
Prices are estimates and may vary based on final dimensions and material selection.
Discover how 3D printing is reshaping industries with cost-efficient manufacturing processes and enhanced design flexibility. This guide explains the various cost components in 3D printing, helping businesses, hobbyists, and engineers optimize their projects for affordability and efficiency. Explore how machine time, material consumption, post-processing, and bulk pricing factor into the final price, complete with practical examples and formulas.
Machine time is one of the most significant contributors to 3D printing costs. It represents the amount of time the printer operates to complete a job. Machine time costs vary depending on the type of 3D printer, its hourly operating rate, and the print time, which is influenced by layer height, part size, and design complexity.
A desktop FDM printer with an hourly rate of ₹20/hour takes 10 hours to complete a small prototype.
Machine Time Cost = ₹20/hour × 10 hours = ₹200
An industrial FDM printer with an hourly rate of ₹50/hour takes 6 hours to print a detailed part.
Machine Time Cost = ₹50/hour × 6 hours = ₹300
 Impact of Resolution: Higher print resolutions
require thinner layers, increasing the print time and
cost.
Impact of Resolution: Higher print resolutions
require thinner layers, increasing the print time and
cost.
 Cost Optimization: Adjusting layer height can
balance quality and print time, significantly reducing
costs.
Cost Optimization: Adjusting layer height can
balance quality and print time, significantly reducing
costs.
 Use Case Differences: Desktop printers are
cost-effective for prototyping, while industrial printers
excel in production-quality prints.
Use Case Differences: Desktop printers are
cost-effective for prototyping, while industrial printers
excel in production-quality prints.
Material cost is a critical component of 3D printing expenses. This includes the primary material used for the part and any additional material required for support structures. Support structures, often necessary for complex designs or overhangs, can account for 10-25% of total material usage. The type and cost of material—be it thermoplastics, resins, or metals—also influence the overall expense.
A part with a volume of 83 cc is printed using PLA at ₹6/gram. Weight would be about 103 grams. Support structures add 15% to material usage. It takes around 10 hours to print.
Material Cost = (103/gram × ₹6/gram) × (1 + 0.15)
Material Cost = ₹618 × 1.15 = ₹710.7
Printer Cost = ₹10/hour × 10 = ₹810.7
A resin part with a volume of 50 cc is printed using engineering resin at ₹40/cc. Support structures add 20%.
Material Cost = (50 cc × ₹40/cc) × (1 + 0.20)
Material Cost = ₹2,000 × 1.20 = ₹2,400
 Material Selection: Engineering-grade materials
are costlier but offer superior mechanical
properties.
Material Selection: Engineering-grade materials
are costlier but offer superior mechanical
properties.
 Support Minimization: Redesigning parts to
minimize overhangs can significantly reduce material
costs.
Support Minimization: Redesigning parts to
minimize overhangs can significantly reduce material
costs.
 Efficiency Gains:Choosing lightweight materials
with high strength-to-weight ratios can optimize costs
while maintaining performance.
Efficiency Gains:Choosing lightweight materials
with high strength-to-weight ratios can optimize costs
while maintaining performance.
Post-processing adds the final touch to 3D-printed parts, enhancing their appearance, durability, and functionality. Tasks like support removal, sanding, polishing, curing, and painting contribute to post-processing costs. Labor rates and time requirements for these activities vary based on the material and complexity of the part.
A PLA part requires 1 hour of support removal and 0.5 hours of sanding. The labor rate is ₹100/hour.
Post-Processing Cost = ₹100/hour × (1 + 0.5) = ₹150
An SLA part requires 2 hours for polishing and curing. The labor rate is ₹200/hour.
Post-Processing Cost = ₹200/hour × 2 hours = ₹400
 Automation Potential: Automated support removal
systems can lower labor costs and improve
efficiency.
Automation Potential: Automated support removal
systems can lower labor costs and improve
efficiency.
 Material Impact: Materials like ABS, which can be
smoothed with acetone vapor, require less labor-intensive
finishing.
Material Impact: Materials like ABS, which can be
smoothed with acetone vapor, require less labor-intensive
finishing.
 Surface Quality Goals: Adjusting print settings to
improve surface finish can reduce post-processing time and
cost.
Surface Quality Goals: Adjusting print settings to
improve surface finish can reduce post-processing time and
cost.
The total price of a 3D-printed part is the sum of the following components. This comprehensive calculation provides a clear breakdown of expenses involved in producing a 3D-printed part.
1. Machine Time Cost.
2. Material Cost.
3. Post-Processing Cost.
Bulk pricing leverages economies of scale by applying dynamic pricing models based on the quantity ordered. As the order volume increases, per-unit costs decrease due to discount curves applied to material and processing costs.
A PLA part wights 103g and the print time is about 10 hours. For one part the price is ₹810.7.
Bulk Price for 500 units = ₹570 per part
 Dynamic Discounts: Higher quantities lead to
progressive discounts on material and processing costs,
reducing the overall cost per unit.
Dynamic Discounts: Higher quantities lead to
progressive discounts on material and processing costs,
reducing the overall cost per unit.
 Material-Specific Pricing: Each material type and
technology (FDM, SLA, SLS, MJF) has tailored pricing
functions for accurate bulk cost estimation.
Material-Specific Pricing: Each material type and
technology (FDM, SLA, SLS, MJF) has tailored pricing
functions for accurate bulk cost estimation.
 Efficiency Gains: Larger orders optimize print and
post-processing time, enhancing cost efficiency.
Efficiency Gains: Larger orders optimize print and
post-processing time, enhancing cost efficiency.
Ideal for small projects and quick prototypes with fast turnaround.
 Minimum Quantity(1-50)
Minimum Quantity(1-50)
 Material Assistance
Material Assistance
 24/7 Support
24/7 Support
 Fast delivery
Fast delivery
 Prototyping
Prototyping
 Concept testing
Concept testing
 Small orders
Small orders
Perfect for mid-scale production with cost-effective options and reliable support.
 Min. Qty: 50-1,000
Min. Qty: 50-1,000
 Bulk pricing
Bulk pricing
 Material guidance
Material guidance
 Quick delivery
Quick delivery
 Functional tests
Functional tests
 Short-run manufacturing
Short-run manufacturing
 Product launches
Product launches

Comprehensive services for scaling ideas to market-ready mass production.
 CAD design
CAD design
 Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering
 Min. Qty: 1000-10000
Min. Qty: 1000-10000
 Full support
Full support
 Large-scale production
Large-scale production
 End-to-end design
End-to-end design
 Custom projects
Custom projects